Calibration of PLC weighing systems is essential to maintain their performance and reliability.
Understanding PLC Weighing Systems
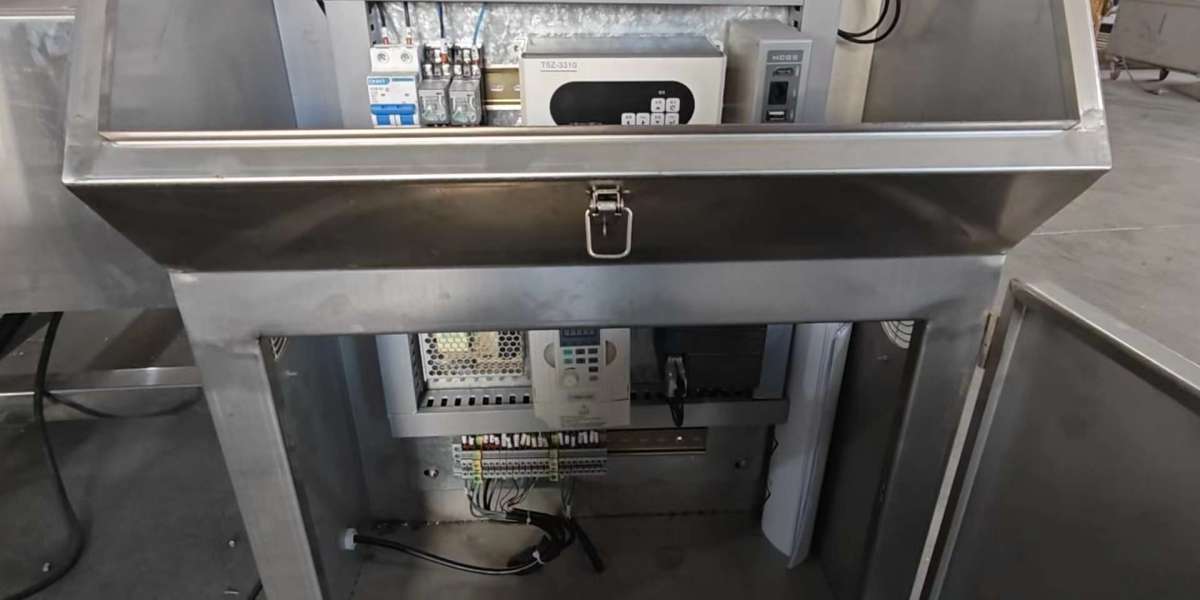
PLC weighing systems typically consist of a load cell, a PLC, and a display or indicator. The load cell converts the weight of an object into an electrical signal, which is processed by the PLC. The PLC then calculates the weight and displays it on the indicator.
Importance of Calibration
Accuracy: Calibration ensures that the PLC weighing system provides accurate weight measurements. Inaccurate measurements can lead to errors in production processes, quality control, and inventory management.
Consistency: Regular calibration helps maintain consistent performance over time. This is especially important in industries where precise weighing is critical, such as pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
Compliance: Many industries have specific regulations regarding weighing accuracy. Calibration is often a requirement for compliance with these standards.
Calibration Process
Preparation: Gather the necessary equipment, such as standard weights, calibration tools, and documentation. Ensure that the weighing system is clean and free of obstructions.
Verification: Verify that the load cell and associated components are functioning correctly. This may involve checking for electrical continuity and performing basic tests.
Standard Weight Preparation: Prepare standard weights of known accuracy. These weights should cover the entire range of the weighing system.
Calibration: Place each standard weight on the weighing platform and record the reading displayed by the PLC. Compare the recorded values to the known weights. If there is a discrepancy, adjust the PLC's calibration settings accordingly.
Documentation: Document the calibration process, including the standard weights used, recorded readings, and any adjustments made. This documentation is essential for maintaining a record of the system's performance.
Frequency of Calibration
The frequency of calibration depends on several factors, including:
Usage: Systems that are used frequently or in harsh environments may require more frequent calibration.
Criticality: If the weighing system is used for critical processes, such as quality control or pharmaceutical manufacturing, more frequent calibration may be necessary.
Regulatory Requirements: Some industries have specific regulations regarding calibration frequency.
Tips for Effective Calibration
Use High-Quality Standard Weights: Ensure that the standard weights used for calibration are traceable to national standards.
Follow Manufacturer's Guidelines: Refer to the manufacturer's instructions for specific calibration procedures and recommendations.
Train Staff: Train operators and maintenance personnel on proper calibration techniques.
Maintain Calibration Records: Keep accurate records of calibration activities, including dates, results, and any adjustments made.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your PLC weighing system provides accurate and consistent measurements, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of your operations.