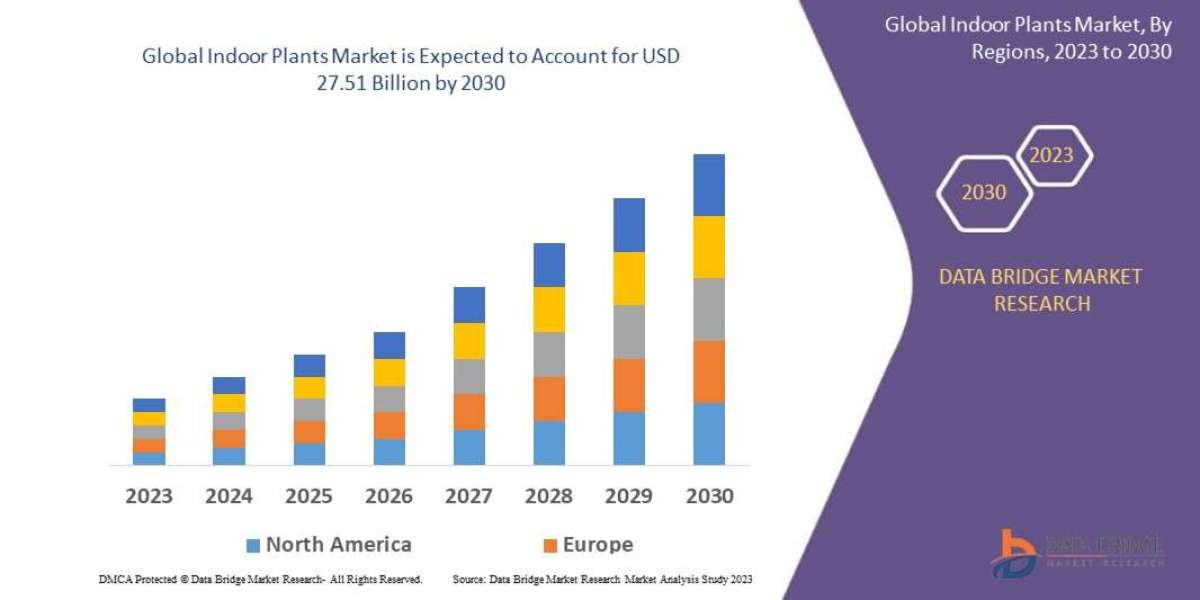
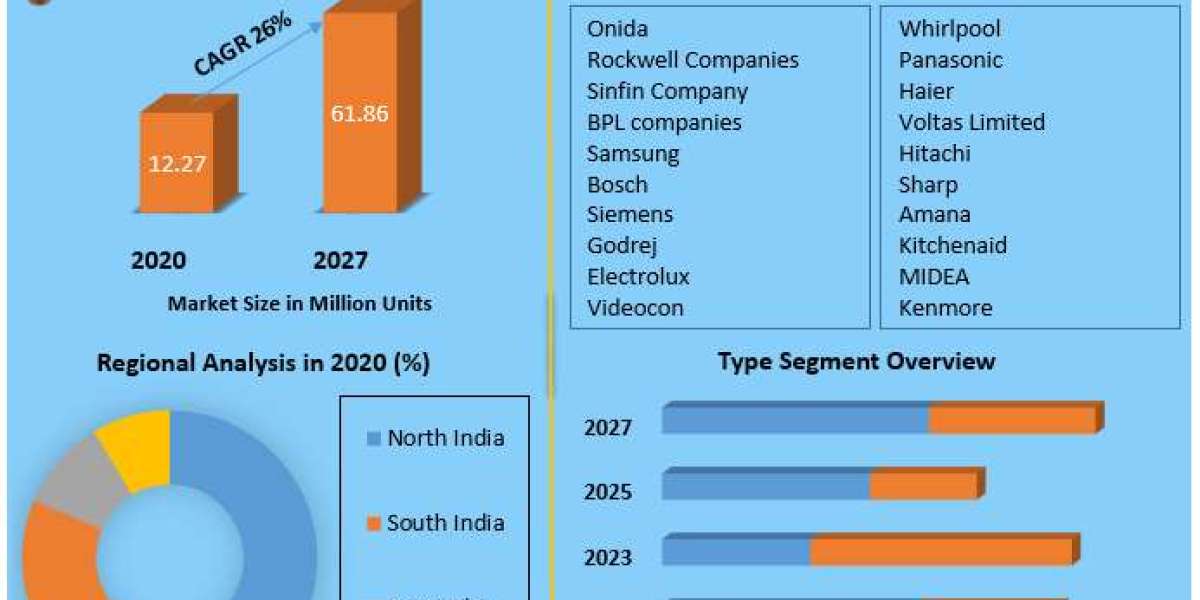
Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR) conductors are widely used in power transmission and distribution systems, particularly for long-distance overhead lines. The conductor is composed of a core of steel strands surrounded by layers of aluminum. The steel core provides mechanical strength, while the aluminum strands ensure high conductivity. This unique combination of materials allows ACSR conductor to effectively balance the need for strength and conductivity, making them ideal for specific applications where these properties are critical.
Advantages of ACSR Conductors
High Tensile Strength: The steel core in ACSR conductors provides superior tensile strength compared to all-aluminum conductors. This is particularly advantageous in long-distance power transmission lines, where the conductor must span large distances between towers without sagging excessively. The high tensile strength ensures that the conductor can withstand the mechanical stresses imposed by wind, ice, and other environmental factors.
Improved Conductivity: While the steel core offers strength, the surrounding aluminum layers provide excellent electrical conductivity. Aluminum, although not as conductive as copper, is lightweight and more cost-effective, making it a practical choice for large-scale power transmission. The combination of steel and aluminum in ACSR conductors ensures a balance between mechanical durability and electrical performance.
Lightweight: ACSR conductors are lighter than equivalent copper conductors, which makes them easier to handle during installation. The reduced weight also means that the transmission towers and other supporting structures do not need to be as robust, leading to cost savings in infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness: Aluminum is more affordable than copper, and the use of steel further reduces costs. The lower material cost, combined with the reduced infrastructure requirements due to the conductor’s lighter weight, makes ACSR conductors a cost-effective solution for long-distance power transmission.
Versatility in Application: ACSR conductors come in various sizes and configurations, allowing them to be tailored to specific needs. Whether the priority is higher strength, greater conductivity, or a balance of both, ACSR conductors can be customized to meet the demands of different transmission scenarios.
Challenges and Maintenance of ACSR Conductors
Despite their advantages, ACSR conductors are not without challenges, particularly when it comes to maintenance. Understanding these challenges is key to appreciating why ACSR conductors are still preferred for long-distance transmission despite these issues.
Corrosion: One of the primary concerns with ACSR conductors is the potential for corrosion, especially in coastal or industrial areas where the air contains higher levels of corrosive elements like salt or industrial pollutants. The steel core, if not properly protected, can corrode over time, leading to reduced mechanical strength and the potential for conductor failure.
- Mitigation: To combat corrosion, the steel core is often galvanized, which involves coating it with a layer of zinc. This zinc layer acts as a sacrificial barrier, corroding in place of the steel. However, the galvanization process can only delay corrosion, not prevent it entirely. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity of the conductor.
Sagging: Over time, ACSR conductors can experience sagging due to the creep (permanent deformation) of the aluminum strands. Sagging is particularly problematic in long-span transmission lines, where excessive sag can lead to reduced ground clearance, posing a safety hazard and potentially causing outages.
- Mitigation: Proper tensioning during installation is crucial to minimize sagging. Additionally, the use of higher-grade aluminum alloys with lower creep rates can help reduce this issue. In some cases, conductors may be re-tensioned or re-conductored to restore proper clearances.
Thermal Expansion: ACSR conductors expand and contract with changes in temperature, which can lead to mechanical stress over time. This thermal cycling can cause the aluminum strands to loosen around the steel core, further exacerbating issues like sagging and reducing the conductor's overall lifespan.
- Mitigation: Choosing the appropriate conductor size and configuration for the expected thermal load is essential. Additionally, thermal expansion can be managed by proper line design, including the selection of towers and insulators that accommodate the expected range of conductor movement.
Vibration and Aeolian Vibration: ACSR conductors are susceptible to wind-induced vibrations, particularly aeolian vibrations, which occur when the conductor vibrates at a frequency induced by steady, low-speed winds. Over time, these vibrations can cause fatigue damage to the conductor and its attachments, leading to potential failures.
- Mitigation: Dampers are often installed on the conductors to absorb and dissipate the energy of these vibrations, reducing the mechanical stress on the conductor. Additionally, proper design and tensioning can help minimize the occurrence of damaging vibrations.
Why ACSR is Preferred Despite Higher Maintenance
Given these challenges, one might wonder why ACSR conductors are still the preferred choice for long-distance power transmission. The answer lies in their unique combination of strength, conductivity, and cost-effectiveness, which makes them ideally suited for this application.
Cost-Effective Solution for Long Distances: ACSR conductors provide a cost-effective solution for transmitting electricity over long distances. The combination of aluminum's lightweight and conductivity with the steel core's strength means that fewer and less robust towers are needed, leading to significant cost savings in the overall infrastructure.
Ability to Span Long Distances: The high tensile strength of ACSR conductors allows them to span greater distances between towers without sagging excessively. This is particularly important in remote or rugged areas where placing additional towers would be difficult or prohibitively expensive.
Adaptability to Environmental Conditions: ACSR conductors can be adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, from the cold climates where ice loading is a concern to hot desert areas where high temperatures can affect conductor performance. By selecting the appropriate conductor type and configuration, utilities can tailor ACSR conductors to meet specific regional challenges.
Long-Term Performance: While ACSR conductors do require regular maintenance to address issues like corrosion and sagging, they offer long-term performance that is critical for the reliable transmission of electricity. With proper maintenance and periodic upgrades, ACSR conductors can remain in service for decades, providing a stable and dependable transmission path.
Technological Advancements: Advances in materials science and conductor design have led to the development of new types of ACSR conductors with improved performance characteristics. For example, the introduction of aluminum-clad steel cores has enhanced corrosion resistance, while new alloy formulations have reduced sagging and thermal expansion issues. These advancements continue to make ACSR conductors a viable choice for modern transmission systems.
Conclusion
ACSR conductors are preferred in long-distance power transmission due to their balance of strength, conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. Despite the higher maintenance requirements, their ability to span long distances, adaptability to various environmental conditions, and long-term performance make them an essential component of power transmission infrastructure. As technology continues to evolve, ACSR conductors are likely to remain a cornerstone of power transmission systems worldwide, providing reliable and efficient service for years to come.