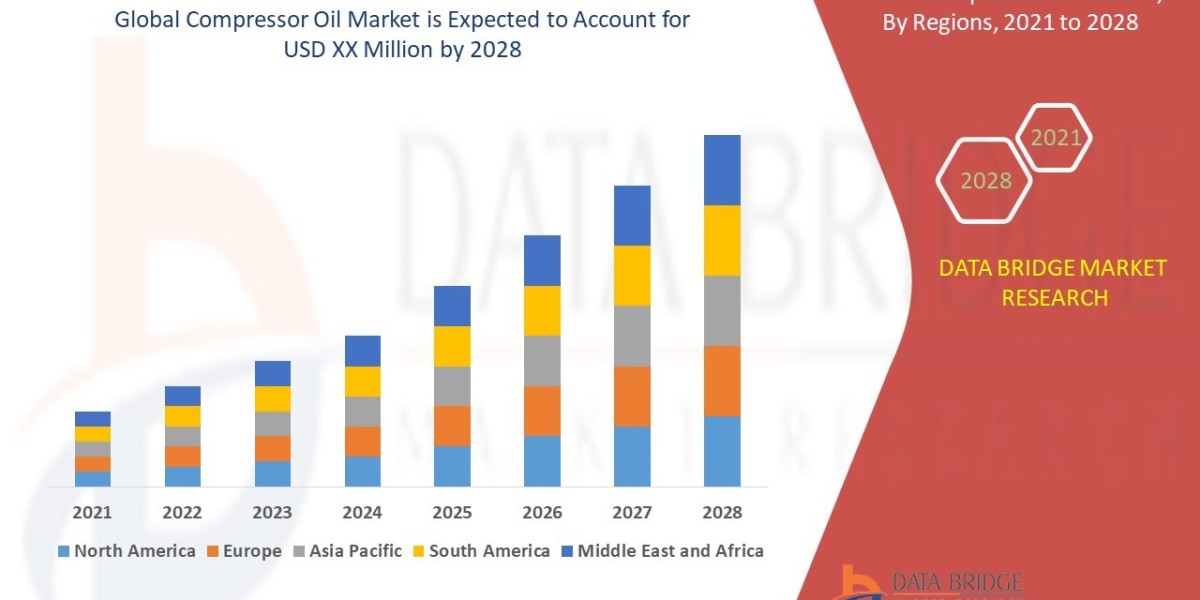
What is ADHD?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning and development. But what is ADHD? It is essential to understand that ADHD is not merely a childhood disorder; it can continue into adulthood, affecting various aspects of life, including work, relationships, and self-esteem.
Symptoms of ADHD
ADHD symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Generally, they are categorized into two main types: inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. Here are some common symptoms:
- Inattention: Difficulty sustaining attention, frequent careless mistakes, and trouble organizing tasks.
- Hyperactivity: Fidgeting, excessive talking, and difficulty remaining seated in situations where it is expected.
- Impulsivity: Interrupting others, difficulty waiting for one's turn, and making hasty decisions without considering the consequences.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and support.
Diagnosis of ADHD
Diagnosing ADHD involves a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional. This process typically includes:
- Clinical interviews with the individual and their family.
- Behavioral assessments and standardized rating scales.
- Gathering information from teachers or caregivers.
It is important to note that there is no single test for ADHD. Instead, the diagnosis is based on a combination of observations and reports from multiple sources. If you suspect that you or someone you know may have ADHD, seeking a professional evaluation is a critical step.
Treatment Options for ADHD
Once diagnosed, various treatment options are available to manage ADHD symptoms effectively. These may include:
- Medication: Stimulants and non-stimulants can help improve focus and reduce impulsivity.
- Behavioral Therapy: This approach focuses on modifying specific behaviors and developing coping strategies.
- Educational Support: Tailored educational plans can assist students in managing their symptoms in school settings.
Combining these approaches often yields the best results. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to determine the most effective treatment plan.
Conclusion
Understanding ADHD is vital for those affected by the disorder and their families. By recognizing the symptoms, pursuing a proper diagnosis, and exploring treatment options, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. If you are looking for more information on ADHD and its management, consider visiting  for resources and support.
for resources and support.